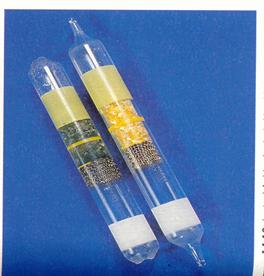
Iron(s) + Copper(II)sulfate(aq)
is a redox reaction.
|
3. Indirect Redox reactions; |
|

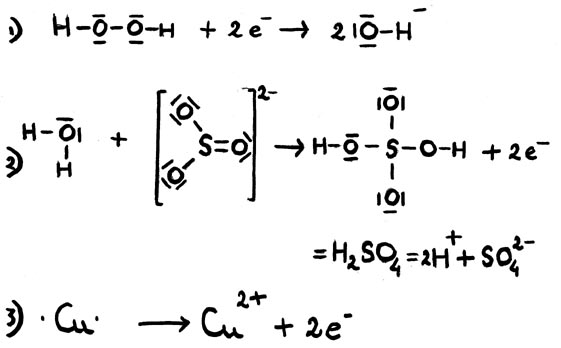
| The equation of couple 1: | red 1 | ox 1 + electrons | |
| The equation of couple 2: | ox 2 + electrons | red 2 | |
| Total equation: | red 1 + ox 2 | ox 1 + red 2 |
| The equation of couple 1: | Al | Al3+ + 3e- | | x 2 | |
| The equation of couple 2: | I2 + 2e- | 2I- | | x 3 | |
| Total equaition: | 2Al + 3I2 | |
2Al3+ + 6I- |
| couple 1: | red 1 | ox 1 + electrons | |
| couple 2: | ox 2 + electrons | red 2 | |
| Total equation: | red 1 + ox 2 | ox 1 + red 2 |



| N2 | is the normal Nitrogen gas, colourless and odourless. |
| NO + NO2 | the 'nitrous vapors', yellow brown, suffocating |
| N2O |
a colourless gas, in fact a kind of nerve affecting gas.
It causes strange face contractions (kind of laughing) and it helps to anaestethise people (or animals). It was found in 1860 and applied, for example, by dentists. |


| Oxidator | Reductor | |
| H2O2+ 2H+ + 2e- | 2H2O | |
| O2 + 2H+ + 2e- | H2O2 |
| oxidatoren | reductoren | |
| Cu+ + e- | Cu | |
| Cu2+ +2e- | Cu | |
| Cu2+ + e- | Cu+ |
| Oxidatoren | reductoren | |
| PbO2(s) + SO42-+ 4H+ + 2e- | PbSO4(s) + 2 H2O | |
| Pb2++2e- | Pb(s) | |
| PbSO4(s)+2e- | Pb(s) + SO42- |
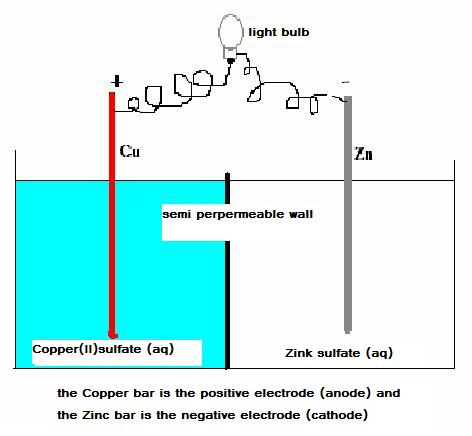

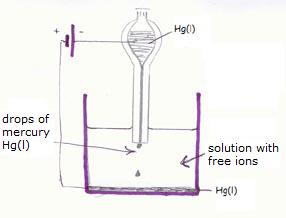
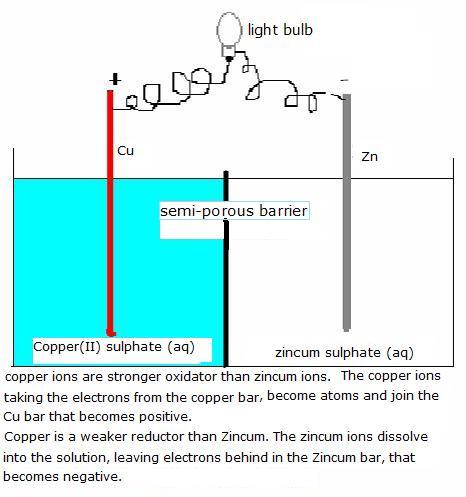
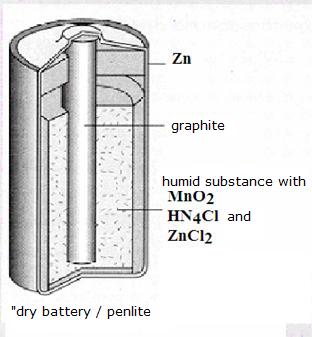
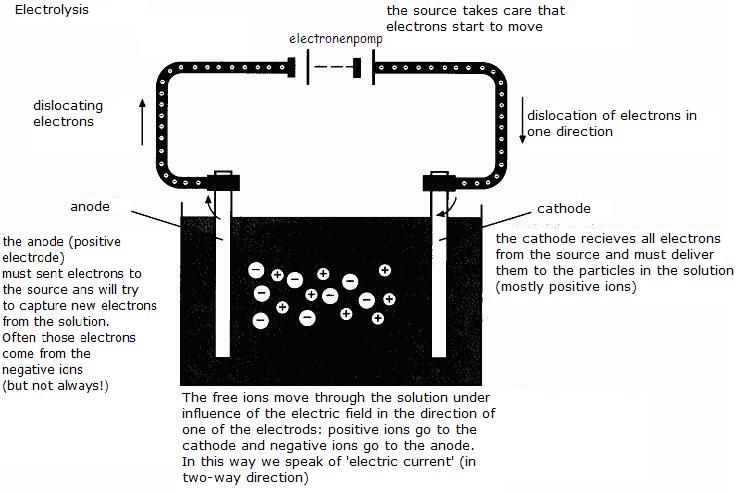

| Direct | Indirect | |
| strong | spontaneous reactions |
dry and wet batteries
go on |
| weak |
nothing effective
happens |
electrolysis and
charging of batteries |
| Without electrodes | With electrodes | |
| 1. design a scheme of what happens, of what is done. | ||
|
2a. Make a list of all present substances / particles, including electrodes
2b. Define the reductor and the oxydator (underline them) |
||
| 3. give the half reaction equations |
3. give the half reaction equations
OX reacts at the positive electrode RED reacts at the negative electrode |
|
| 4. make all equations certain | 4. make all electrode equations certain | |
| 5. check possible secondary reactions | ||
| 6. Write down your observations and conclusions | ||
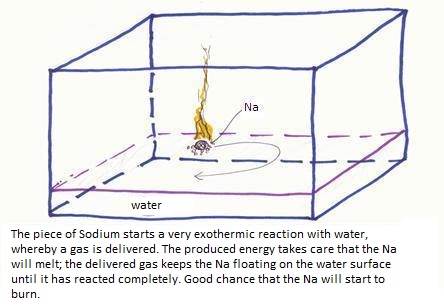
| Red: | Na | Na+ + e- | |x2 | |
| Ox: | 2H2O + 2e- | H2 + 2OH- | |x1 |
 2Na+ + H2 + 2OH-
2Na+ + H2 + 2OH-