To get loose molecules of Sulphur, the molecules must get out of the molecular lattice of Sulphur; after that, the 8 atoms in one molecule S8 must separate, get loose from each other.
S8(s)
- Fe2+ and S2-
- FeS
|
You know that all substances are built up with particles. The most simple particles are atoms or ions. (thats where we stay for now)
Those particles - normally - do nog stay alone, but connect to other particles. That can happen in different ways, but they always approach and connect at their exterior, their outside; so you can imagine that this must involve the outer electron shell, orbital and the valency electrons in that shell. Only the atoms of noble gases can remain 'bachelor'. They normally do not connect to other particles. Every way to connect particles we call that a chemical bond. That is the main topic of this module. The character of such chemical bonds has big consequences for the properties of the substance. |
The IONIC bond = attraction between positive and negative particles. |
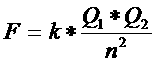

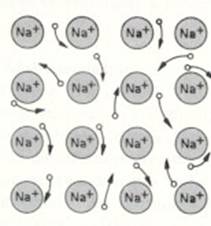
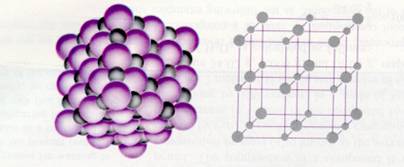
Metallic bond = attraction between (negative free) electrons and (positive) metal ions in a lattice |
|
Question 6 is a practical task
[a practical task must be done in groups.] You must try to resolve a number (8) of tasks according to a pattern of (ten) questions (question list). First you have an example (reaction of Iron with Sulphur). With that example we discuss all the questions. So you know what to do at all 8 tasks. This time you don't need a lab. Its all theory, paper work.
Every time the question is if the two substances do react and, if yes, what you may know about the chemical bonds between the two. You must study every reaction according to the question list below.
|
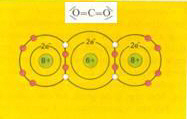
Covalent bond = sharing of each others electrons |



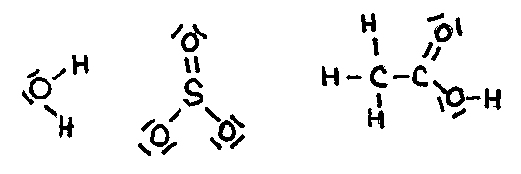
| mono | 1 | di | 2 | tri | 3 | tetra | 4 | penta | 5 |
| hexa | 6 | hepta | 7 | okta | 8 | nona | 9 | deka | 10 |
| CO | (mono)carbon mon(o)oxyde |
| CO2 | (mono)carbon dioxyde |
| P2O5 | (di)phosphor pent(a)oxyde |
| P2O3 | (di)phosphor trioxyde |
| N2O | NO | N2O3 | CuCl | PbS | SO2 |
| I | II | III | IV | V | VI | VII | VIII | |
| 1 | H | He | ||||||
| 2 | Li | Be | B | C | N | O | F | Ne |
| 3 | Na | Mg | Al | Si | P | S | Cl | Ar |
| 4 | K | Ca | Ga | Ge | As | Se | Br | Kr |
| 5 | Rb | Rb | In | Sn | Sb | Te | I | Xe |
| 6 | Cs | Bi | Tl | Pb | Bi | Po | At | Rn |
| 7 | Fr | Ra |
| metals | Cs |
| metalloids | Po |
| non-metals | Se |
| Metalic bonds | many metals have a low value of E |
| Ionic bonds | ΔE: > ±1,6 |
|
Covalent bonds
- covalent, non polar - covalent, polar |
0 < ΔE < ±1,6
0 < ΔE: < ±0,4 ΔE: > ±0,4 |

| CS2 (ΔE = ±0) | CO2 (ΔE = ±1.0) | H2O (ΔE = ±1.3) |
| Covalent bondings | Covalent bondings | Covalent bondings |
| Non polar molecules | Non polar molecules | Polar molecules |
| There is no dipole | There is no dipole | There is a dipole |
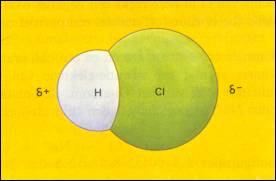
| There are no δ+ and δ- |
There are δ+ and δ- of which the central points do overlap |
The central points of δ+ and δ- do not overlap each other (remain at a distance) |
|
S=C=S
|
O = C = O
δ- δ+ δ- |
δ+
δ+
H H \ / O δ- |


| simple: | Na+ Cl- H+ |
| complex: | H3O+ OH CO32- |
H-H |
- 4.36 | H-F |
- 5.63 | N≡N |
- 9.45 | C-F |
- 4.4 |
F-F |
- 1.53 | H-Cl |
- 4.32 | C≡C |
- 8.3 | C-Cl |
- 3.3 |
Cl-Cl |
- 2.43 | H-Br |
- 3.66 | C≡N |
- 8.9 | C-Br |
- 2.8 |
Br-Br |
- 1.93 | H-I |
- 2.99 | C=O |
- 8.0 | C-I |
- 2.4 |
I-I |
- 1.51 | H-O |
- 4.646 | C=S |
- 2.6 | C-O |
- 3.5 |
H-O (alkanol) |
- 4.5 | N-H |
- 3.9 | C=C |
- 6.1 | H-S |
- 3.44 |
C-C |
- 3.5 | C-H |
- 4.1 | O=O |
- 4.98 | P-H |
- 3.22 |
|
Question 28 is an action task:
[this action task must be done in groups. Sometimes you can realise the task in a lab] The reactions below have been treated before. You must now treat every reaction according to the question list with six questions.
|