Possess one or more carboxylis groups (-COOH) (more about this in module 11)
You must know some specials: carbonic acid, fatty acid, amino acid, phenol.
The carboxylis group can donate an ion H+, or, the carboxylic group is an acid (mostly a weak acid)
The hydroxy group normally does not donate H+, only if this one is connected to a benzene ring (phenol)
For more information about organinic acids, see the module 9 and module 11 about these topics.
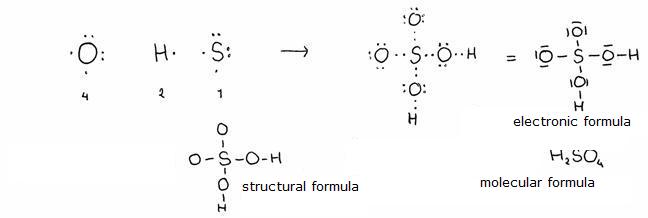
They are the non-organic acids containing the element Oxygen.
Mostly can be made of, starting with the right oxyde (like: sulfur trioxyde with water --> sulfuric acid).
these acids can vary in nomenclature, depending on the minimal and maximal number of oxygen atoms in the molecule (that has to do with the so called oxydation number (see module 10). So you have H2SO3 and H2SO4
Also the conjugated basesof these acids get an own name.
example:
phosphoric acid = H3PO4. (is made of P2O5 with H2O)
If the formula is not H3PO4, but H3PO3, then this acid is called: phosphorous acid.
| Acid | Acid ion | example | example |
| hypo.......ous acid | hypo.......ite | hypochlorous acid | hypochlorite |
| ......ous acid | ......ite | chlorous acid | chlorite |
| ......ic acid | ......ate | chloric acid | chlorate |
| (hy)per.......ic acid | (hy)per.......ate | (hy)perchloric acid | (hy)perchlorate |
N.B.
Not all oxygen containing acids have all four options
But they all have the normal '...ic acid' and '....ate'
Some have also the '....ous acid' and the '....ite'
Hypo and hyper are rather exceptional
Best known of this type is HCl, hydrochloric acid
The formula starts always with H, immediately followed by another element, without Oxygen (HBr, HI, HCN, etc.)
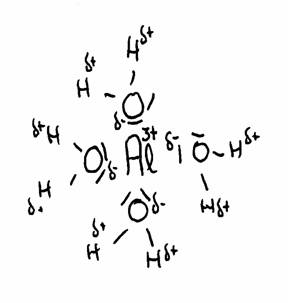
The most famous example is the Aluminium ion dissolved in water, but there are lots more. Cations normally are hydrated polypositive metal ions: Al(H2O)63+, Cu2+, Fe2+ of Fe3+, any many more, and always hydrated in water.
hydratation
The poly positive ions attract closely, in watery environment, the negative sides of the water molecules.Then they cause a repulsive feeling between the central positive ion and the δ+)charges of the H atoms of the water molecules. There is a tendency to repulse H+.
A solution of, for example Iron(III)chloride can obtain in this way a rather acid pH value.
The drawing shows the attraction between Al3+ and the δ- part of Oxygen and the δ+ part of Hydrogen.
The water molecules (6 in total) surround the 3+ ion of Aluminium, because this positive ion attracts the δ- of water.
thus the distance between 3+ and δ+ becomes shorter, and with that, the repulsion between 3+ and δ+ becomes stronger.
The concequence is that the H can be (more of less) repelled. There could be even donation of H+ ionen, and all this we call: an acid character. (much more about this in module 9)
Question 9
Explain the acid character of the ammonium ion in water, just by writing the reaction equation.
Goto answer 04-09
Normally the negative ions like to attract H+ ions (so the normally are bases).
Yet there are certain negative ions that can serve as acid and tend to donate H+. Example: HCO3-.
Question 10
The negative ions that can serve as acid, must be amphoteric. Explain this statement with a reaction equation.
2.2 Different types of bases
There are also different types of bases, maybe weak, maybe strong:-
Organic molecules
You can think of amines, and of amino acids (see module 11)
-
Negative ions
In principle, all negative ions can receive, capture H+ ions. So they are always bases, strong or weak.
-
some positive ions
Those cations, after having donated H+, can take back that H+ ion and thus act as a base.
- Some neutral molecules; more hereover later.
More information about acids and bases can be found in module 9.
Question 11
- Give the structure of a triprotonic organic acid.
- Give the structures and names of five amphoteric particles.
- In the table with acids and bases, which formulas belong to the cations?
- Statement: "acids met negative charge are always ampholytes." Is that true? Explain.
-
Given the following substances: kitchen salt, chalk, dry and hydrated Carbonhydroxyde, soda.
Do these substances contain acids or bases?
2.3 Molecules
In the nomenclature of moleculers, we often use prefixes: mono, di, tri, etc.Example: N2O4 is called: di nitrogen tetra oxyde.
The use of prefixes is limited to those situation where confusion can occur if the prefix is left out.
prefixes you should know:
mono, di, tri, tetra, penta, hexa, hepta, octa, nona, deca
Example:
"carbon oxyde" is not enough as name, because there are two of them: CO and CO2
CO is called carbon mon(o)oxyde and the other is carbon dioxyde. The o in brackets mostly is left out.
Molecules of an element with Hydrogen often get a traditional name like ammonia, water, natural gas, and more.
In the organic chemistry (carbon chemistry) thereis a very extended system with prefixes.
Meta, eta, propa, buta and then further as known already: penta, hexa, nona, deca etc.
More about this further on.
After all this: there are salts, that, included in an ionic lattice, contain water molecules. But they remain solids! They contain water molecules and we call them: hydrates.
example: Copper(II)sulphate pentahydrate; and another example: Na2CO3.10H2O.
Question 12
Table XI shows the "solubility of salts in water".
With this table, combining positive and negative ions, make at least 20 different combinations and give them names and formulas.
Question 13
Any real chemist knows these ions in the table by heart. Just do it.
3. The Carbon atom
For several reasons the Carbon atom is very special:- every Carbon atom can make four bondings, which is more than other atoms can.
- The Carbon atom connects easily to other Carbon atoms. Silicon can do that more or less, but normally 'atoms don't like that'. Most atoms prefer to connect with atoms of another type. There is a preference rule for connecting different elements. Except for Carbon however.
To understand all this, you need to go into the story of 'orbitals'. Two orbitals of Carbon atom are important for the making of bonds: the sublevels 2s and 2p.
These orbitals can cooperate in various ways (when making bonds). They also can mix and thus form 'hybrides' :sp3, sp2, sp.
Below a try out to make this clear:
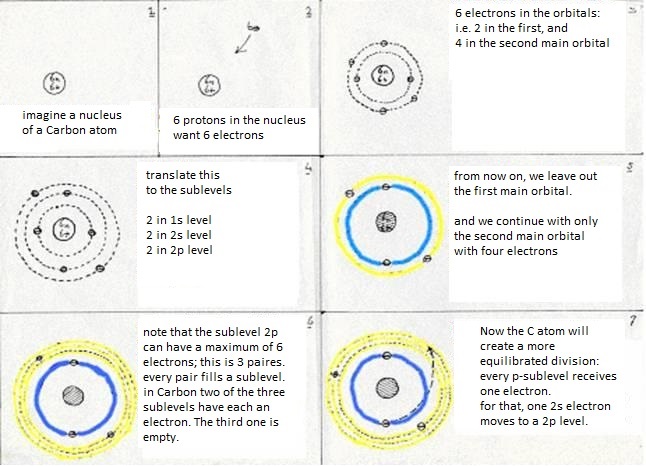
The sublevels of Carbon are: 1s2 2s2 2p2
The first main level 1s2 suffers no change at all, whatever the Carbon atom does. But in the second main level occurs a kind of reorganisation:
The four valency electrons (two s and two p) have found a way to come to a more stable situation:
- first: a 2s electron becomes a 2p electron (so goes a bit further away from the nucleus, which costs energy)
- then: 2s1 becomes 2p3 (this change also costs energy)
-
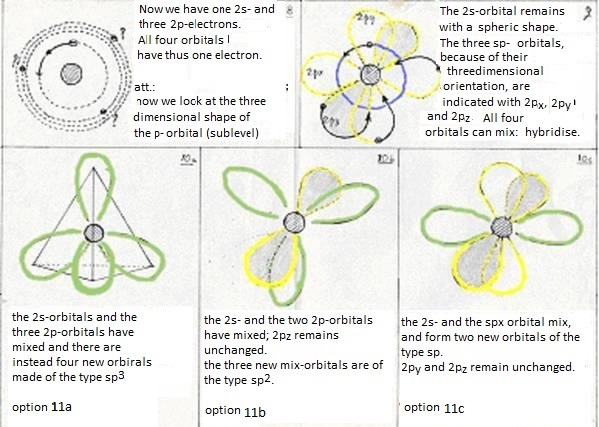
at last: the four levels will now mix and form hybrides. Or: one 2s-orbital and three 2p-orbitals participate in this hybridisation.
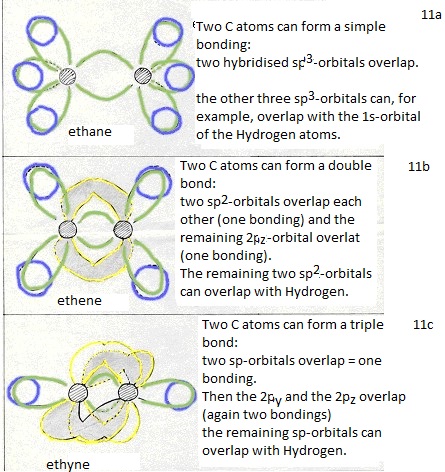
They form four new orbitals of the type sp3 (here energy is set free = exothermic). These four new and equal orbitals are responsible for the four (similar, equal and simple) bondings of a Carbon atom.
Besides this sp3-hybridisation exist another two options:
- The first (just explained above) is the hybridisation of a 2s-orbital with three 2p-orobitals to four new orbitals of the type sp3
-
Now the second option is that one 2s- and not three, but only two 2p obitals participate in the hybridisation.
Then three new orbitals are made of the type sp2
and one old 2p-orbital remains unchanged; that one can take care of an extra bonding.
(double bond: 1 bonding is of the type σ and one bonding is then π). -
The third option is that one 2s-orbital and one 2p-orbital participate in the hybridisation.
Then two new orbitals are made of the type sp and two old 2p-orbitals remain;
thus a triple bond can be made between two C atoms (one bonding σ and two of π).
In benzene and similar substances, every C atom had three orbitals of the type sp2 that per C atom forms three σ-bondings. In that case, per C atom in a benzene ring is one 2p-orbital and in total 6 per ring. They overlap in such a way that they stabilize the molecule with a very special 'fourth' bonding of the type π (aromatic).
Question 14
Study the following strip drawings, that try to explain again the special C atom.
the Hydrogen atom, very different from the Carbon atom, is the most simple atom with only one electron. The electron division is: 1s1.
Nothing to hybridise here. The s-orbital has a round shape and can overlap with any other type of orbital of whatever other atom (in carbon chemistry mostly a Carbon atom)
This overlap always gives a σ-bonding and always delivers only a simple bond.
Question 15
Explain why Hydrogen only forms simple bonds.
Question 16
What means the symbol: sp2 (explain that in your own words)
Question 17:
What kind of bonding types do we meet in a molecule of propene?
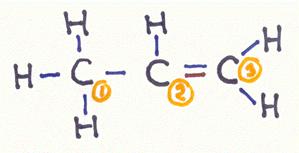
Goto answer 04-17
4. Carbon Chains
4.1 Introduction
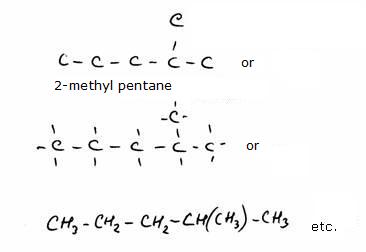
The amount of substances in the organic chemistry (carbon chemistry) is unimaginable large.
The most important reason for that is the opportunity of Carbon atoms to connect to each other and thus to form short or very long carbon chains. A good nomenclature (namegiving)with basic rules for all those chains is absolutely necessary.
those chains can be met in chemistry books in different ways. Sometimes they are drawn very detailed, with every atom visible, sometimes you meet them as a kind of skeleton where not all atoms and/or bonds are shown.
Without knowledge of the basic rules it is not possible to understand the famous 'international nomenclature'.
4.2 Main chains and branches
As a consequence of its special charactyer, the C atom can form chains with simple, double, triple or even cyclic bondings, not only with Carbon, but with many other atoms.There are so many different molecules based on the Carbon atom that a carbon chemistry has been introduced. In the old days (but you still meet that word often) we called that organic chemistry.
primary, secundary, tertiary en quaternary
The structure below shows 'methyl butane' at the left and 'dimethyl propane' at the right side.Cabon atoms that are only connected to one other C-atom are called: primary C-atoms/ they always are situated at the end of a carbon chain.
C-atoms in between two others, we call secondary C-atoms.
Thus we also have tertiary C-atoms, connected to three others, and even quaternary ones, surrounded by four other C-atoms.
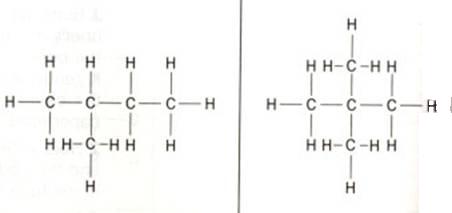
Question 18
How many primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary C-atoms are in the two structures?
The words primary etc. are not exclusively used for the C-atoms. Also other atoms or atom groups can have this qualification.
For example, if one OH-group is connected to a secondary C-atom, we speak of a secondary alcohol, or a secondary hydroxy group.
In proteins you also will find those concepts primary etc. but then they mean something different.
Question 19
Answer the following questions about the structures A, B, C and D:
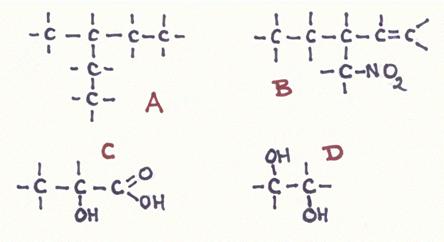
- Give the official name of every structure
- How manyu secondary C-atoms has every structure?
- Do you somewhere see a secondary OH-group? if yes, where?
- Are all main chains also the longest chain?
Goto answer 04-19
4.3 Nomenclature
Question 20Which specific groups do you recognize in the structure?
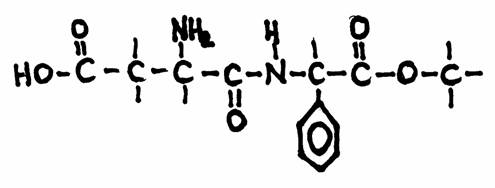
This is the structure of 'aspartame', a substitute for common sugar for persons that must take care (diabetici, of people afraid of becoming fat).
Aspartame has an effect 100 times stronger than common sugar:
1 g of sugar can be replaces by 10 mg Aspartame.
Other substitutes are: fructose (1,7x suiker) and sacharine (400x sugar)
The organic substances always contain a main chain of Carbon atoms.
In the nomenclature the fist thing to do is: search and recognize the main chain.
-
Always chose as a main chain:
- the longuest possible chain, but at the same time:
- the chain containing possible double or triple bonds.
- The main chain can have brances or functional groups, like an OH-group
- If necessary, we add numbers to indicate to what position in the main chain the brance, the special bond of the functional group is connected. Always try to achieve the lowest possible numbering.
Rules for the nomenclature, in this case for aliphatic hydrocarbons
Every Carbonic compound has a main name, based on the number of C atoms in the main chain:
on the dots appear suffixes:
- ane: the main chain only has simple bonds.
- ene: the main chain also has double bonds.
- yne: the main chain also has triple bonds.
- yl: this is used when talking about a branch, not a main chain.
| Prefixes: | |
| Hydroxy | Means: an OH group connected to a Carbon chain |
| Alkoxy | A side chain (branch) connected via an O atom to the main chain (ether) |
| amino | a NH2-group connected to the main chain. |
| nitro | a NO2-group connected to the main chain |
| Suffixes: | |
| ol |
Just as in hydroxy: an OH-group at the main chain.
The OH-group has thus two options for nomenclature. |
| al | an O atom is connected with a double bond to a primary C of the main chain |
| on | en O atom is connected with a double bond to a secondary C of the main chain |
| acid | means that a carboxylic group (COOH-) is connected to the main chain |
| (o)ate |
The H of the carboxylic group was donated (and can be replaces by something else, or is negative)
Could be the rest of an acid, but also an ester |
| ose | a combination of al or on with some ols |
Amina = one or more Hydrogen atoms of ammonia were replaces by alkyl groups.
- All before mentioned rules are also true for polymers; just the prefix 'poly' is needed extra.
-
That means nothing else than 'many'.
Polymers always are built up of small units, small molecules that - in large numbers - are connected to each other, and form the polymers. - Those small units are called 'monomers'. (mono = 1; poly = many)
- In general we may say that the name of a polymer is simply the same name as that of the monomer, but with the prefix 'poly'.
Examples:
Propene is a molecule with a chain of three C atoms with one double bond.
The positions of double and triple bonds, if necessary, are indicated with numbers.
3-etyl is a branch, a side chain of two Ca atoms, and is connected to the third C of the main chain.
Apart from the suffixes, there are many prefixes:
-
Mono, di, tri, tetra, penta, hexa, hepta, octa, nona, deca
they indicate 1 to 10 and give the number of a certain group. -
Cyclo
here the main chain is not linear, but circular.
Example: 3,4-dimetyl,1-hexene:
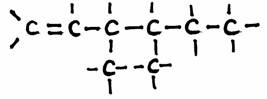
N.B
H atoms can be left out in the structural formulas.
Question 21
Now you should work as much as possible with models, and try to build the following molecules:
methane (the threedimensional shape is here calles: tetraeder); petrol (the most important isomere of octane; ethene; ethyn, to be used in welding processes)
The hydrocarbons can be found in earth layers, deep in the earth crust, or under the see or ocean. You find them in:
- crude oil
- natural gas
Later we come to all connected processes, in other modules. This is only about nomenclature.
De homolous series
Such a series contains substances with one kind of functional group, with the same general formula and with similar properties.Example: all alcohols have an OH-group, and a general formula CxHyOH. But: you have also ethers and esters etc.
The differencies between the membersof a homologous series depend on the length of the carbon chain CxHy and other data.
Methanol, for example, will evaporate much easier than propanol. But chemically they show very simmilar reactions.
(un)saturated
A carbon chain can be saturated or unsaturated, depending on the presence of double or triple bonds between C atoms.Later we return to the typical reactions of unsaturated bonds (that can be 'opened' to become saturated; something is added).
4.4 Models

Talking about nomenclature of chemical substances, it is unavoidable to talk about models.
In chemistry, we use various models to visualize this topic (the threedimensional shape of molecules).



model box types of models C6H12O6
Never ever forget that a model is nothing more than just a very simplified image of the reality. Nover draw more conclusions out of a model than the makers of the model want to explain with it. A model is always a simplification.
But, on the other hand, a good model really helps in better understanding why chemical substances behave this or that way. You should have a model box.
Question 22
Make the models shown above.
Question 23
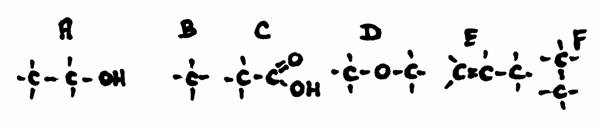
- Which structure is unsaturated?
- Which substances belong to the same homologous series?
- Which substance react with Sodium carbonate?
Question 24
given the following structure:
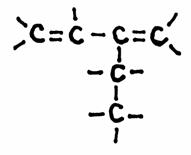
- Which name has this chemical structure?
- Check if the models of this structure (in the pictures) are okay.
- Compare them wich each other. Give your comment on every model.
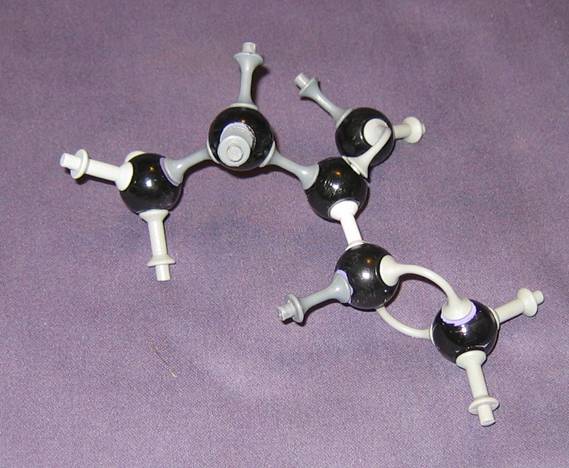
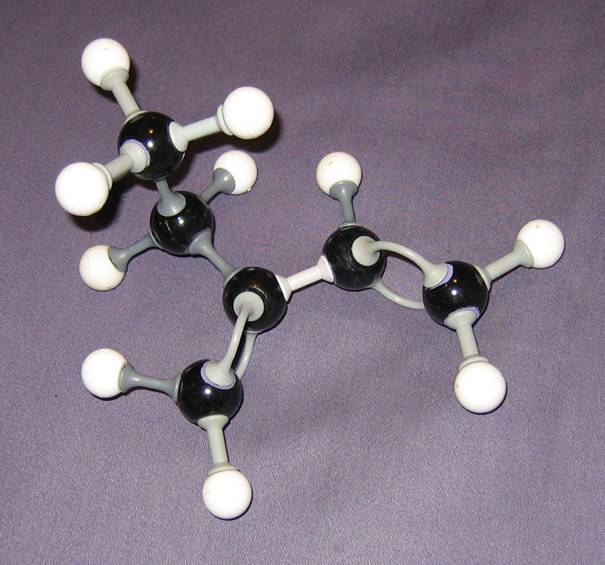


Goto answer 04-24
5. Carbon compounds with oxygen and Nitrogen
5.1 Organic compounds with Oxygen
Question 25This is a task to use models: construct with molecular models the following molecules: ethanol; aceton; formaline; acetic acid; etanediacid (=oxalic acid); an ether group and an ester group.
Question 26
Are the following statements true or false? Explain your answer.
- 2-hidroxy,2-methylpropane is the same as 1-methyl,2-propanol.
- 2-hydroxy,2-methylpropane is a tertiary alcohol.
5.2 Organic compounds with Nitrogen
Question 27
Of an ammonia molecule were substituted:
- 1 H-atom by an ethyl group
- 1 H-atom by a methyl group
- 1 H-atom did not change at all
- This molecule has the name trimethyl amina
- this molecule is a secondary amina
Question 28
Give the official name of Valine (one of the amino acids)
Goto answer 04-28
4.3 Plastics; synthetic polymers
This topic belongs to "macromolecules". We will talk about them in the paragraph with biochemistry, toghether with the natural polymers.Here we limit the words to some synthetic polymers made by men in factories:
plastic, nylon, artificial rubber, polyether, polyester, and poly-additie products (PVC for example)
some rules:
- All before mentioned rules are also true for polymers; just the prefix 'poly' is needed extra.
-
That means nothing else than 'many'.
Polymers always are built up of small units, small molecules that - in large numbers - are connected to each other, and form the polymers. - Those small units are called 'monomers'. (mono = 1; poly = many)
- In general we may say that the name of a polymer is simply the same name as that of the monomer, but with the prefix 'poly'.
Structure of the polymers
-
- homopolymers: the macromolecule is built up of only one type of monomers.
- copolymers: the macromolecule is built up of two or more types of monomers.
-
- a macromolecule can have a linear structure; the product then is more flexible.
- a macromolecule can have a branched structure; the product is then harder, with little or no flexibility.
-
-
Between the macromolecules can exist interconnections. Such products remain hard when heated. We call them "thermoharders".
These substances can have a kind of lattice, a threedimensional structure with interconnections.
-
If not,the structure has no clear threedimensional structure; there is no such thing as a lattice.
At heating, the product becomes then softer and can sometimes even melt. We call them "thermoplasts".
-
Between the macromolecules can exist interconnections. Such products remain hard when heated. We call them "thermoharders".
These substances can have a kind of lattice, a threedimensional structure with interconnections.
Applications
| Polyethene | Plastic bags |
| polypropene | plastic chairs |
| polyvilnyl chloride (PVC) | plastic tubes for plumbing |
| silicon (chain of Si and O with alkyl groups) | siliconen kit |
| nylon (polyamide) | cloths |
| synthetic rubber | car tires |
| polyester and polyether | matrasses |
6. Isomeria
A molecular formula often gives some of the structure of the molecule, but is not sufficient to know immediately the whole structure.Example: wat is the structure of C3H7OH?
This probably will be 1-hydroxy propane, but: 2-hydroxy propaan is also possible.
More difficult is: C3H8O.
This could also be one of the hydroxy propanes, but why not methoxy ethane?
And one of the OH-groups of gluces (C6H12O6), at what side of the molecule is it connected?
Again: knowledge of the molecular formula not automatically is enough to understand the structure.
Even one molecular formula can have more than one structures. In that case we talk about 'isomeria'.
We distinguish various types of isomeria, amongst them:
-
Structural-isomeria
- position isomeria
- chain isomeria
- functional isomeria
-
Stereo-isomeria
- Cis-trans-isomeria
- Optical isomeria
Question 29
Explain if the following statements are true or false:
- simple alcohols (with one OH-group) are functional isomers with ethers.
- acids are not isomers with esters.
- propanal and propan-1-ol are structural isomers
Question 30
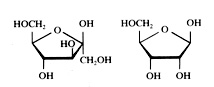
Have a close look at the two structures of glucose:
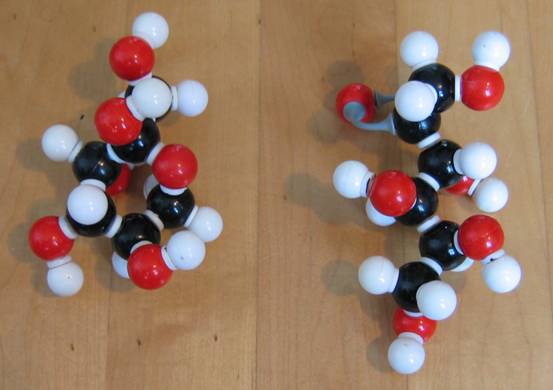
C6H12O6 C6H12O6
Write the two structures on paper to discover that one is linear and the other cyclic. What is the functional group that is present in de linear, but not present in the cyclic structure?
Below another photo. But now with different types of models (the connection pieces are different).
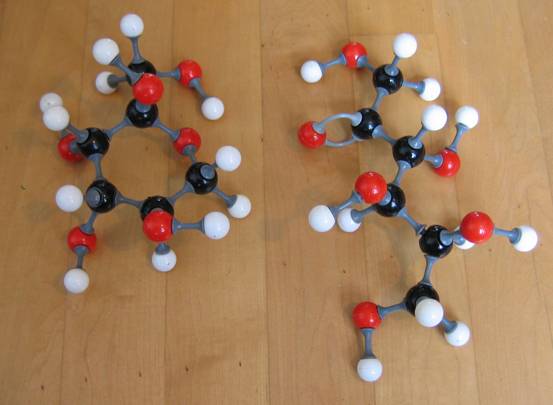
Note that in the first model type the double bond cannot be imitated with the right connection pieces!!
6.1 Optical isomeria
The word 'optical' indicates that molecules of this type of isomeria have special properties connected to optics.Every organic substance having one or more C atoms connected to four different atoms or atom groups, had 'optical activity': the can turn a vibration plane of monochromatic light, to the left or to the right.
This phenomena can be measures with a polarimeter. The atom connectedto four different groups acts like that and is called an "optic active centre".
 |
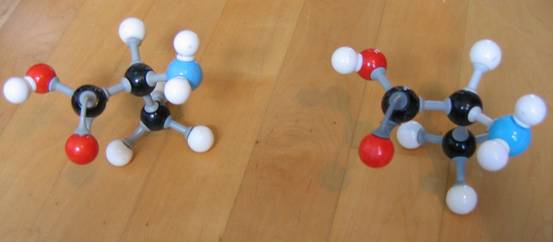 |
|
| D-alanine L-alanine | D-alanine D-alanine | |
| they are each others mirror image |
they are equal, but not each others mirror image |
Question 31
Try to build the two optical isomers of the amino acid Alanine, with models, and thus to visualize the optical isomeria.
Question 32
Look carefully at the following structures:
1.
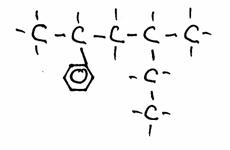
2.
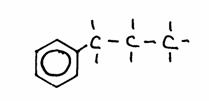
3.
- Give the names of every structure. Att.: there may be more possibilities.
-
Are the structures 2) and 3) isomers? Yes or No?
Explain your answer.
Goto answer 04-32
More information about steriochemistry can be found in websites like: shapes in organic chemistry
7. Nomenclature of Biochemistry
Biochemistry may not be absent in a nomenclature course. Every year it becomes more evident how chemistry influences body and soul. There is so much happening in (human) metabolism: everything obeys the laws of chemistry.
"It is all chemistry."
The nomenclature in the world of biochemistry is not simple, but yes obeys the normal rules for nomenclature.
Here we do not handle with the complicated names of medicines, for example. We look at the simple things.
The human body is built up of chemical compounds, all of them being in a non stop dynamic situation. They continuously suffer changes.
They change position, they are diluted of concentrated, they react with each other, they leave, they come, etcetera.
Many names of these substances are very well known by the public, like carbohydrates, proteins and fats.
Any chemist must know something more than the names of these three; think of structures, properties, reactions.
But this chapter is limited to the nomenclature. The rest comes later.
In general we distinguish four important groups of biochemical substances:
- Saccharides (carbohydrates, glycides)
- Lipids (oils and fats)
- Proteins
- Nucleic acids(DNA RNA)
In fact, biochemistry belongs to organic chemistry, but there are so many special substances part of living organisms, in particular the macromolecules, that there is sufficient reason to dedicate a special paragraph to names in biochemistry.
We talk about substances in living creatures (men, animals, plants). In this chapter we focus on men. And structures of vitamines, hormones, and medicines etc. stay out.
7.2 Carbohydrates, saccharides
Question 33The concept "carbohydrates" as historically made up in natural sciences, but is, in fact, a wrong word.
Explain this statement.
The saccharides can be considered as C-chains with aldehyde or keton groups, combined with some OH groups.
The suffix to recognize them is ....ose.
They serve as energy rich food.
Mono-, di-, (oligo-) and polysaccharides
Examples:- glucose and fructose
- sacharose and maltose
- amylose and cellulose in plants, and glicogene in animals
Question 34
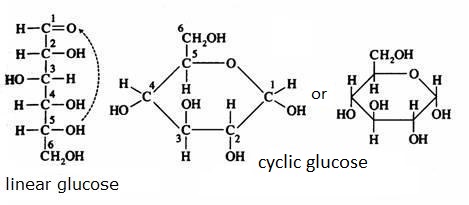
Check the formula C6H12O6 in the images below.


the cyclic structure of glucose
- Can you recognize the structure of the aldehyde group?
- Can you recognize OH groups in the structure?
- Does the substance contain non symmetric C atoms, or: is this substanceoptical isomeric?
Mono-, di-, (oligo-) an polysaccharides
Examples:- glucose and fructose
- saccharose and maltose
- amylose and cellulose in plants, and glycogene in animals
Question 35
Control the formula C6H12O6 in the images below:


the cyclic structure of glucose
- Can you recognize the aldehyde group in the structure?
- Can hou recognize the OH groups in the structure?
- Does the substance contain non symmetric C atoms (is the substance an optical isomer?)
Monosaccharides
They are the monomers of the polysaccharides. There are various types of monosaccharides, depending on:- the number of C atoms: tetrose, pentose, hexose, heptose...
- the presence of an aldehyde or a keton group: aldose and ketose
- the structure of the whole molecules, linear or open, or: closed or cyclic.
five examples of monosaccharides:
Glucose α and β Galactose
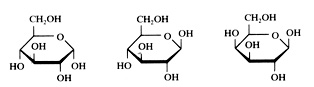
Fructose Ribose
Question 36
To what type or types belongs glucose?
Cyclic or linear
Monomers normally have both structures: cyclic and linear. The two are continuously in equilibrium with each other (supposed that they are dissolved in water). Note that the cyclic structure has lost its specific aldehyde or keton group.But always the ring of the cyclic structure is closed with an O atom that has a position in between two C atoms.
This phenomena has consequencies for the reactivity of the substances.
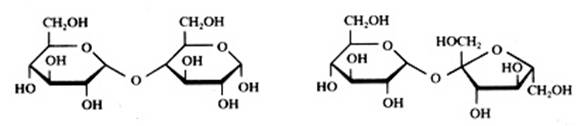
Disaccharides
Disaccharides are "dimers": built up of two monomers having a cyclic or a linear structure. The bonding between these monomers could be called an 'oxygen bridge': you always will note the following bonding: C - O - CExamples:
Saccharose has two rings: one of glucose and one of fructose. In daily life we speak of sugar.
 |
|
Maltose also is built up of two monomers (2 x glucose), of which one can have a linear structure and the other only can have a cyclic structure.
Question 37
Construct a model of a sugar molecule, and write the stuctural formula.
polysaccharides
Hundreds or thousands of monomers, in particular of glucose, participate, are connected and form a very long chain: a macromolecule. In general can be stated that all parts are cyclic.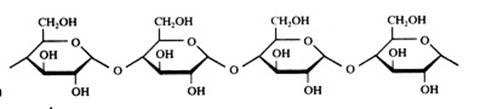
- in plants: amylose or starch, and cellulose
- in human/animal: glycogene
Starch + ion I3-
7.3 Lipids or Fats: glycerol & fatty acids
Talking about lipids, we must realise that we limit ourselves here to vegetalbel oils and animal fats, and that they all have similar kind of basic structure:tri-esters of glycerol (1,2,3-trihidroxypropane) and fatty acids
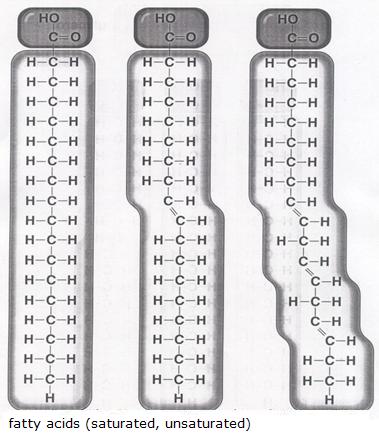
In daily life, de difference between fat and oil is obvious (solid and liquid). Behind this external difference is hidden a chemical difference: unsaturated and saturated fatty acids. The unsaturated substances have a mor liquid character (oil) than the saturated ones (fat).


One molecule of glycerine connects to three molecules of fatti acid. Thus they make one molecule of lipid (fat or oil). Besides that three molecules of water are produced. In the example we probably see an oil.
Question 38
How can you see in the example that the product tends to be an oil?
Question 39
Explain if the molecules of fatty acids are polar or non polar.
7.4 Proteins
(essential) amino acids
The word 'amino acid' indicates what is to be the composition of these compounds:An amino acid contains an amino group (-NH2) and a carboxyl group (-COOH).
The most simple amino acid is 'glycine'.
H2N - CH2 - COOH
In the tables, table 16, you can find all amino acids that participate in the synthesis of proteins.
Question 40
Give the official names of the amino acids Gli, Ala, Leu, Phe and Val.
The human body needs, to make proteins, lots of molecules of amino acids.
Some amino acids can be produced by the body itself, from other substances, but not all amino acids. Those ones the body cannot make itself, must be obtained by the body from outside, so via nutrition.
These ones are called: 'essential amino acids'.
Peptides
Amino acids can form peptide bonds.
When more amino acids participate, you can get a chain of amino acids, wherein every amino acid is connected to another amino acid via a peptide bond.
Thus a polypeptide is produced.
Question 41
With three amino acids (see table XVI for the structures) you can make different tripeptides.
Give the structures.
(Poly)peptides, proteins
Question 41| 1) ---- C - NH - CO - C - NH - CO - C - NH - CO - C - NH ---- |
| 2) ---- C - COO - C - C - COO - C - C - COO - C - C ----- |
| 3) ---- CNH2 - C - O - C - CNH2 - C - O - C - CNH2 - C - O ---- |
| Statement: "Structure 1 shows a protein structure" |
| Is this statement false or true? |
We may stick to the fact that polypeptides in fact are similar to proteins. They always deal with an enormous number of connected amino acids.
Not every polypeptide has to be a natural protein.
Natural proteins always have a secondary and a tertiary structure, and only use natural amino acids.
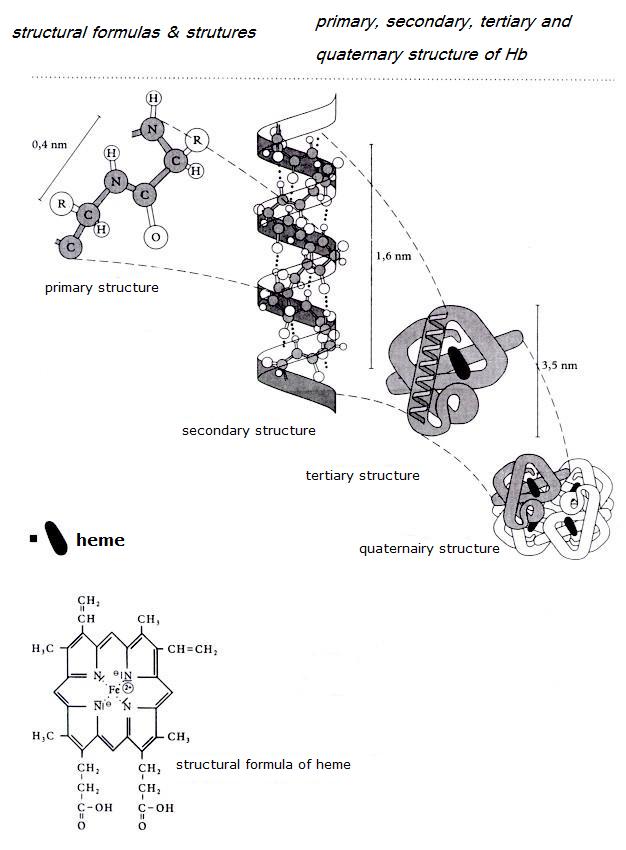
- The primary structure of a protein is the sequence in which all those amino acids are connected within a molecule.
- The secondary structure of a protein is the 'helix' (see image); a spiral form of the primary structure.
- The tertiary structure of a protein is the way how that tertiary structure is threedimensionally folded.
- Sometimes there is an quaternary structure, of various packets of tertiary structure work toghether.
Question 42
In the following structures, indicate the primary, secundary and tertiary structure; and also the position of the 'co-enzym'.
Enzyms belong to the group of proteins (see biology).
Often the enzym-protein-molecules have an active place, a co-enzym, like a heme group in the transport enzym Hemoglobine (see figures).
7.5 DNA
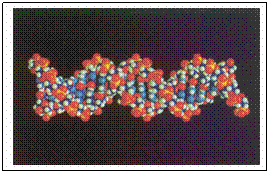
Desoxy-ribo Nucleic Acid
We now talk about the macromolecules (very very macro!!) that occur in the cell nucleus of living creatures. They are the most important part of chromosomes and carry in a chemical way the (genetic) information needed for the functioning of the cell. In particular the formation of proteins is regulated this way.
In quiet status the DNA molecules have a helix structure, better: a double helix (see image)
Question 43
Explain what means the next statement:
The DNA molecules are co-polymers of 4 monomers, and every monomer is represented by a symbol:
A, G, T and C.
Adenosine, Thymine, Guanine and Cytosine are the nucleic acids, the spinal colon for DNA.
This spine is a long chain of alternately a Ribose group and a phosphate group.
The primary structure of DNA can be considered as the sequence of the nucleic acids, just as the amino acids in proteins.
Again like proteins, there is a secondary structure: a helix structure. More: there is a 'double helix', i.e. the molecule is double.
The two parts are kind of mirror image of each other. If they separate, two similar DNA-molecules are made.
During functioning as the manager of the cell, DNA sends information from the nucleus tot the plasm, in the form of RNA (a copy is made of certain parts of DNA)
8. Benzene and benzene derivates
How to approach the structure of benzene? How to look at it? An easy way to do so is starting at the four valency electrons of the Carbon atom.For not complicating, we leave out the orbitals and hybrides (spx).
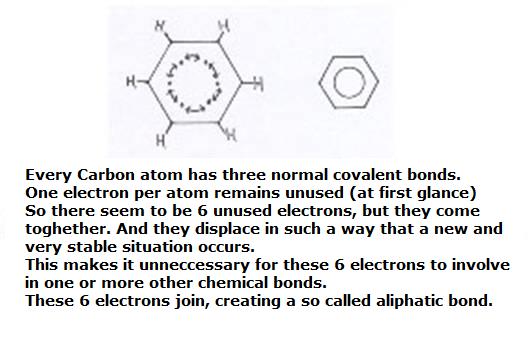
The benzene ring can be considered as built up of six Carbon atoms, every one of them using their valency electrons for bondings with an H atom and two neighbouring C atoms.
You see, then there is of each C atom still one valency electron unused; is still free.
What to do with these 6 free electrons? They toghether form a kind of ring bonding; a ring bond of 6 common C atoms. Here we meet a special bonding that we indicate in structures with a circle. Thus there is a similar bonding between all 6 C atoms of the ring. Okay, it is a bit of easy explanation.
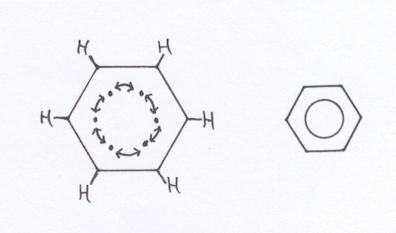
In the better chemistry books you can find lots of more explanation, more precize, with orbirals 2s, 2px, 2py and 2pz.
Those three: 2s and 2px and 2py can mix, and form three new 'hybride-orbitals': sp2.
They are responsible for the formation of two bondings (we talk in term of orbital overlap) with other Carbon atoms and one bonding with a Hydrogen atom of the type σ.
Between every two C atoms there comes an overlap (bond) of 2pz-orbitals. Or: 6 bonds of the type π.
For nomenclature of benzene derivates we chose one of the six C atoms in the ring. That one we call number 1.
Starting from number 1, we count numbers 2 - 6
Question 44
-
Give the structures of
- 1.2-dinitrobenzene
- 3-amino, nitrobenzene.
In the old days (and still in many books) we used prefixes where now we use the numbers 1 - 6.
An example is: 1,2 dinitrobenzene was mentioned (and still you meet this name): ortho-dinitrobenzene (ortho = 1,2 )
- Ortho = 1,2
- Meta = 1,3
- Para = 1,4
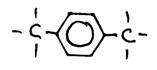
Question 45
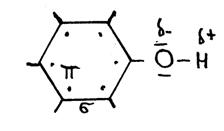
The above structure (C6H5OH) is the structureof "phenol".
- What is the official name?
- Explain every symbol in the scheme.
- Give a simpler structure.
The following needs your attention in nomenclature: phenol and phenyl; be carefull; they are not the same!
Phenol has an OH group at the benzene ring. But if benzene itself is a branch, than we call it 'phenyl'.