The analytical chemistry is:
that part of the chemistry that deals with
analysing, investigating of
chemical compounds and mixtures.
| We can divide the chemical analysis in two kinds of research: | ||
| 1 | The qualitative analysis: | wich substanc(es)? |
| 2 | The quantitative analysis: | how much of every substance? |
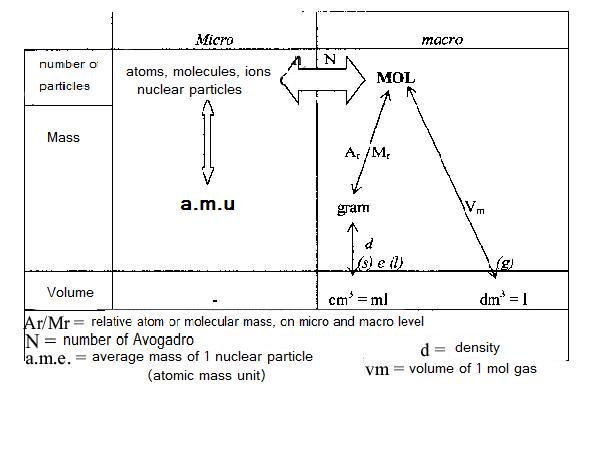
| Particle | Mass (g) | Mass (a.m.u) | Charge |
| Electron | 9,1*10-28 | 0 | -1 |
| Neutron | 1,67495*10-24 | 1 | 0 |
| Proton | 1,67254*10-24 | 1 | +1 |
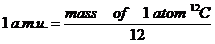
| < Number of Avogadro = 6.1023 |
| < One MOL is 6.1023 |
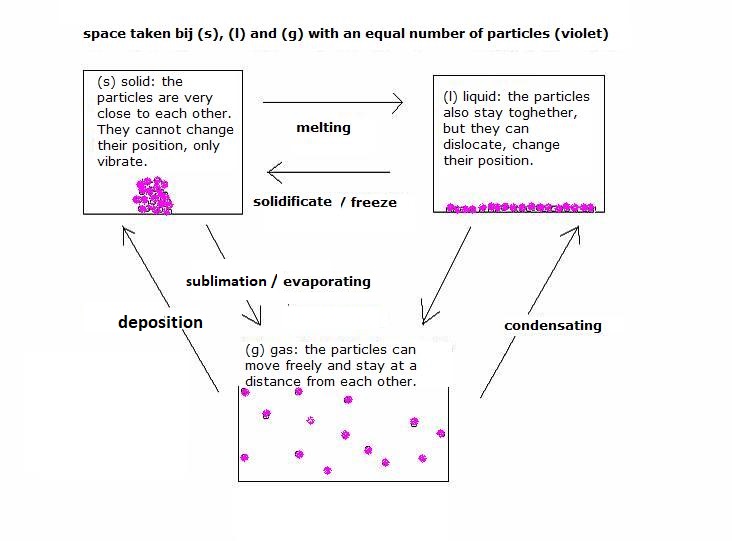

| CO2 | O2 | NH3 | |
| 0°C | 75·10-3 mol/l | 2·10-3 mol/l | 52 mol/l |
| 25°C | 34·10-3 mol/l | 1·10-3 mol/l | 26 mol/l | 100°C | 0.0·10-3 mol/l | 0.7·10-3 mol/l | 0.0 |





|
Definition:
DH = mass of V liter gas (at t and p) mass of V liter H2 (at t and p) |
| 1 | CH4(g) + 2 O2(g) |
| 2 |
Subline those substances about which you have data, or about which is a question. CH4(g) + 2 O2(g)
|
| 3 | So, 1 mol CH4(g) reacts with 1 mol CO2(g) (proportion is 1:1) |
| 4 | 16 g CH4(g) produce 44 g CO2(g) (here we apply the molecular masses) |
| 5 |
in reality we have not 16 g, but only 4 g to be burnt.
The factor to be introduces is: 4/16. 4/16 x 16 g CH4(g) produce 4/16 x 44 g CO2(g) finally: standard circumstances mean: at temp 25°C and pressure 1 atm. Then 1 mol gas = 22.4 liter 1/16 x 44 = 11 gram CO2(g) is produced, that equals 4/16 mol = 4/16 x 22.4 liter CO2(g) = 5.6 liter |
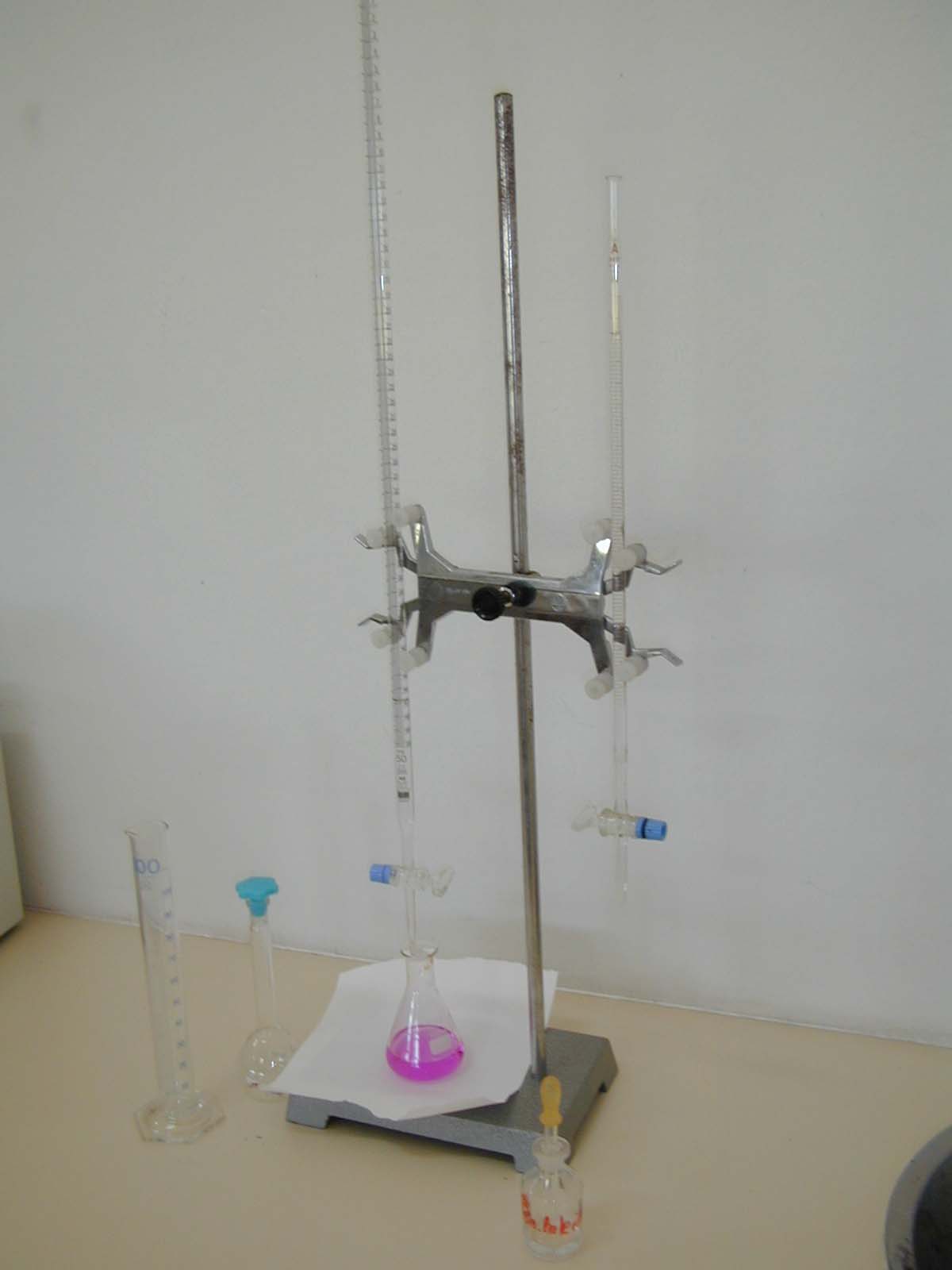


| To be able to observe the endpoint, the changing moment, we often need an indicator | |
| At acid base titration: | an acid base indicator |
| At redox titration: | a redox indicator |
| a weak organic acid | a weak organic reductor |
| HIn |
RedIn |
| HIn has another color than In- | RedIn has another color than OxIn |
| The color of HIn or In- | The color of RedIn or OxIn |
| can only be observed if the equilibrium is sufficiently to the left or the right. | |
|
The color of an indicator depend on the environment:
In acid environment (or in reducing environment) the above equilibria are at the left, so the color of HIn dominates (or the color of RedIn). Per indicator this can vary substantially. |
|
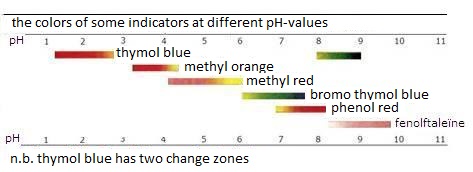
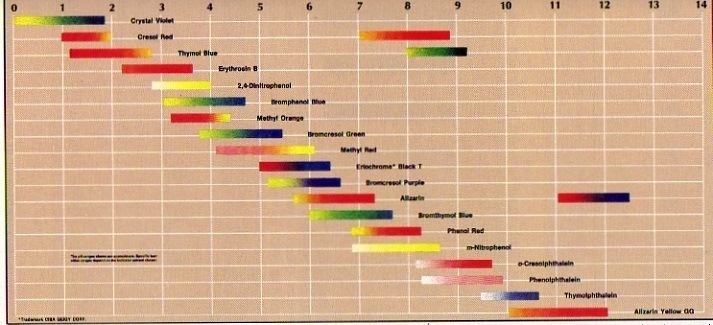
| titration of strong acid with strong base: | pH = 7 |
| titration of strong acid with weak base: | pH < 7 |
| titration of weak acid with strong base: | pH > 7 |
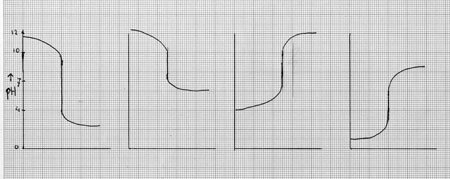
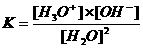

|
|
BUFFER:
A rather concentrated mixture of a weak acid with its weak conjugated base |
![]()
|
The following three experiments
must be executed according to the six points of this action task: |
Take notice, when working on it, that all you do, observe and think (about chemistry of course) and make at the end a report.
Take care that the substance to investigate always remains in stock; never use all of it! Draw conclusions of every observation; that's how a lot of research will turn out to be unnecessary. |
| The 3 action points for every experiment are: | The 3 experiments are: |
|
|
| Execute four experiments according to the four items of the task: |
Every time write what you are doing, what you see, observe and what you think of it (in chemical terms of course), and make at the end a report.
Take care that the substance to investigate always remains in stock; never use all of it! Draw conclusions of every observation; that's how a lot of research will turn out to be unnecessary. |
| the 4 action points for every task are: | The 4 tasks are: |
|
|
| The aim is that your group will execute a number of the titrations below, according to the ten points of this action task, to be done in the right sequence: |
During work, every time write down what you are doing, what you observe, what you think of it, and make a report at the end.
Take care that the substance to investigate always remains in stock; never use all of it! Draw conclusions of every observation; that's how a lot of research will turn out to be unnecessary. |
| The 10 action points for every task are: | The 6 tasks are: |
|
| According to the points I - III you must work in groups and prepare and controll three buffer mixtures. For preparing you can chose from six substances and those three substances must be mixed in the right mol proportions. |
Every time when working, you must write down all you do, observe, think about the procedure.
At the end a report must me made.
Take care that the substance to investigate always remains in stock; never use all of it! Draw conclusions of every observation; that's how a lot of research will turn out to be unnecessary. |
| The 3 action points for every task are: | The 6 tasks are: |
|
|