Isomeria
A molecular formula often shows some of the structure of the molecule, but is not sufficient to know immediately the whole structure.
Example: wat is the structure of C3H7OH?
This probably will be 1-hydroxy propane, but: 2-hydroxy propaan is also possible.
More difficult is: C3H8O.
This could also be one of the hydroxy propanes, but why not methoxy ethane?
And one of the OH-groups of gluces (C6H12O6), at what side of the molecule is it connected?
Again: knowledge of the molecular formula not automatically is enough to understand the structure.
Even one molecular formula can have more than one structures. In that case we talk about 'isomeria'.
We distinguish various types of isomeria, amongst them:
- Structural-isomeria
- position isomeria
- chain isomeria
- functional isomeria
- Stereo-isomeria
- Cis-trans-isomeria
- Optical isomeria
Have a close look at the two structures of glucose:
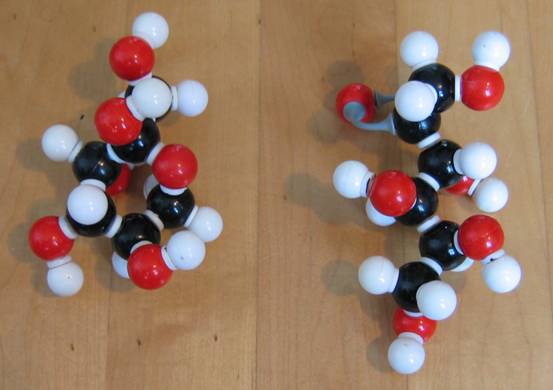
C6H12O6
C6H12O6
You should discover that one is linear and the other cyclic.
Below another photo. But now with different types of models (the connection pieces are different).
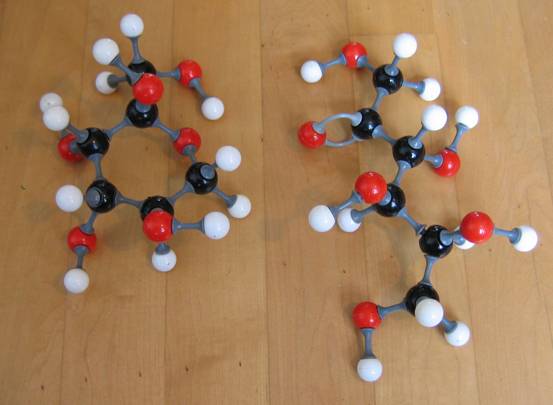
Note that in the first model type the double bond cannot be imitated with the right connection pieces!!

