The equilibrium condition
In module 7 reaction rate was discussed:
V = k.[conc.]n
- V : reaction rate;
- k : a joint venture of the constant factors;
- n : the coefficient of the reactants in the equation;
Applying this formula to the forward and to the backward reaction
2HI  I2 + H2
I2 + H2
we find the following result:
Vforward = kforward x [HI]2
and
Vbackward = kbackward x [I2] x [H2]
Att.: in principle the concentrations of the substances in an equilibrium never become 0; that means that also the rates never become 0. This may only occur in unidirectional reactions.
The reaction rate is rather dependent on the concentrations of the reacting substances:
The more substrate, the faster the reaction.
- at a certain moment there is a maximum rate?
- Below you find diagrammes of rates versus concentrations:
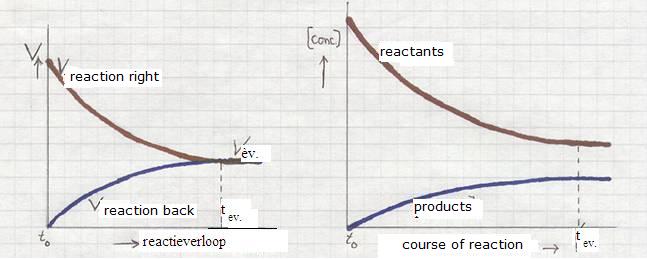
The equilibrium condition of a chemical equilibrium is:
The two reaction never become 0 (remain a certain rate) and have equal rates.
Or: Vforward = Vbackward

