Polar covalent bond, dipole molecules
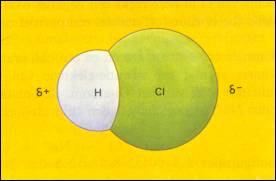
A bond between two of such atoms is called "polar"
|
I |
II |
III |
IV |
V |
VI |
VII |
VIII |
| 1 |
H |
|
|
|
|
|
|
He |
| 2 |
Li |
Be |
B |
C |
N |
O |
F |
Ne |
| 3 |
Na |
Mg |
Al |
Si |
P |
S |
Cl |
Ar |
| 4 |
K |
Ca |
Ga |
Ge |
As |
Se |
Br |
Kr |
| 5 |
Rb |
Rb |
In |
Sn |
Sb |
Te |
I |
Xe |
| 6 |
Cs |
Bi |
Tl |
Pb |
Bi |
Po |
At |
Rn |
| 7 |
Fr |
Ra |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| metals |
Cs |
| metalloids |
Po |
| nont-metals |
Se |
The scheme above is the simple periodic table (limited to the main groups I - VII)
the red zone: the non metals have the tendency to gain electrons and so become negatively charged (big electronegativity)
the blue zone: the metals have a tendency to donate electrons and so become positive (small electronegativity)
